Carbon Footprint New Construction, the European standard for certifying the carbon footprint of buildings
Greenhouse gas emissions derived from construction materials account for over half of a building's emissions over its entire life cycle. This proportion is expected to increase even further with the implementation of the new Energy Performance of Building Directive (EPBD), eventually reaching 100% of net lifecycle emissions.
As these emissions are not regulated in most European countries, the Carbon Footprint New Construction certification system constitutes a basis for calculating, optimizing, and certifying the carbon footprint of buildings constructed in Europe.
Greenhouse gas emissions on the life cycle of the building

How to assess greenhouse gas emissions of buildings?
Embodied Carbon
this scope covers greenhouse gas emissions related to the building's construction materials and technical equipment, assessed over its standardized life cycle (duration of 50 years).
Operational Carbon
the certification system also covers greenhouse gas emissions related to the building's main utilities (heating, cooling, lighting, ventilation, domestic hot water, auxiliaries) during the usage phase.


A certification system aligned with the decarbonization goals of the European Union
A European certification system
The Carbon Footprint New Construction certification system is based on the following guidelines:
The LEVEL(S) European framework governing the assessment of the environmental performance of buildings, and more specifically, their carbon footprint. The assessment can thus be directly used in CSRD reporting or taxonomy.
The British standard PAS 2060 and the international standard ISO 14068 define the framework and minimum requirements for achieving carbon neutrality. There are no legal restrictions on the use of the term “carbon neutrality”, which occasionally leads to its misuse. Compliance with these standards ensures that real efforts have been made and that the project significantly contributes to combating climate change.

Calculate your project's carbon footprint
identify and reduce its impact by assessing the primary sources of emissions.

Aim for carbon neutrality
currently, a project cannot achieve zero emissions. When significant efforts have been made, the scope can then be extended to include off-site environmental projects, in the view of offsetting residual emissions and aiming for carbon neutrality.

Optimize your project
the certification system provides a methodology and benchmark values, guiding you towards a significant reduction in the project's carbon footprint.
How can a construction project meet carbon neutrality?
At the scale of a construction project, carbon neutrality is achieved when there is a balance between positive greenhouse gas emissions (embodied carbon of materials and operational carbon) and negative emissions (related, for example, to material recycling or renewable energy production).


In most cases, the effect of biogenic carbon storage as well as the benefits of on-site renewable energy production and end-of-life material recycling are not sufficient to offset greenhouse gas emissions over the building's life.
The manufacturing and transportation of materials, as well as electricity production, are still heavily carbon-intensive at present. The carbon offset mechanism, outside the project scope, can then be used to achieve a net-zero balance. It also contributes to the fight against climate change in an alternative and complementary way, particularly by increasing carbon sinks.
The carbon pass
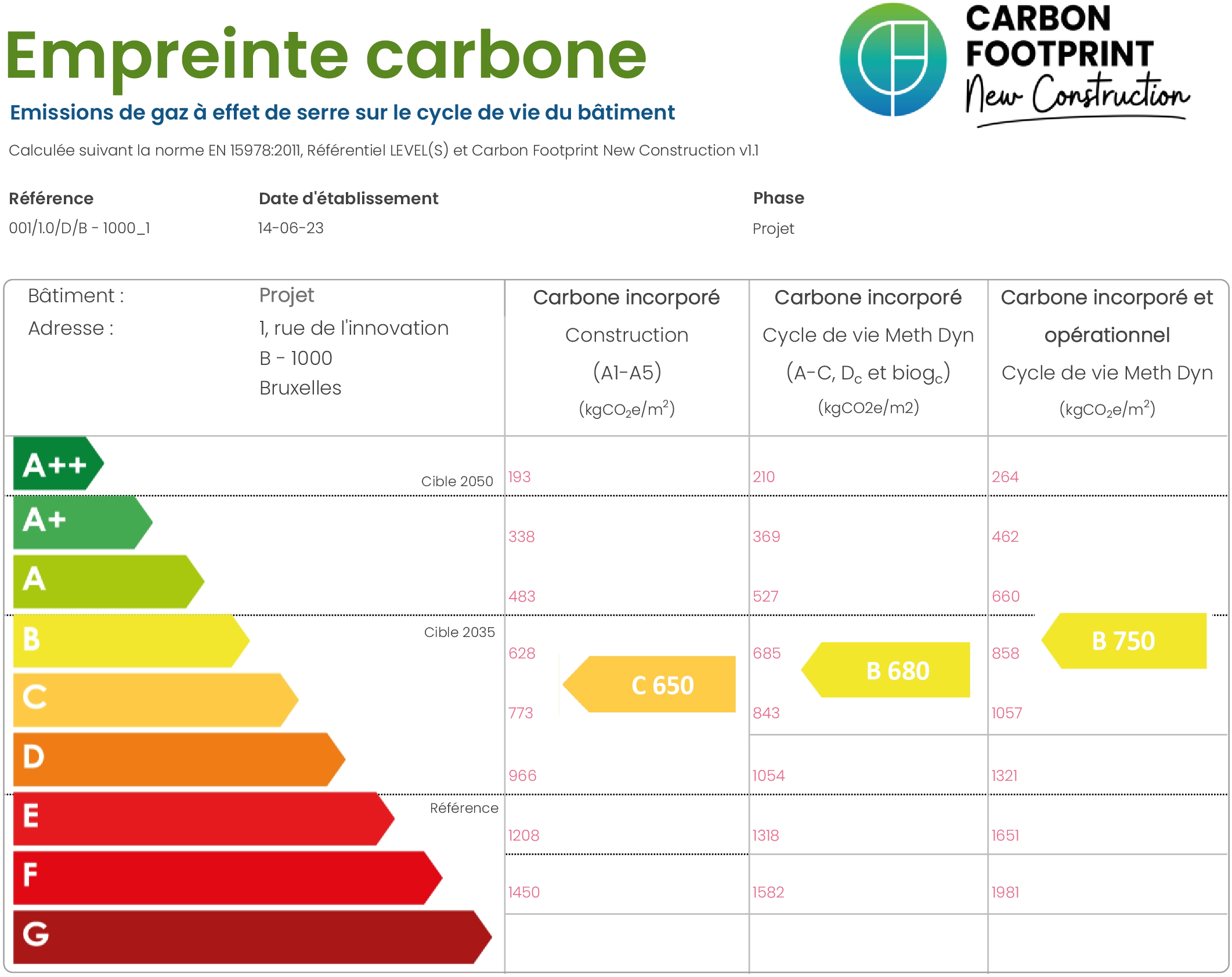
The carbon pass displays the building's performance from the perspective of its impact on climate change, along with the information required for taxonomy and CSRD reporting. The carbon pass presents, in a concise 5-page format, the greenhouse gas emissions of the building, by category and type, highlighting the project’s strengths and areas for improvement.
contact us
Get started today and find out more about our certification system. You will gain all the insights needed to minimize your environmental impact.

